Science Radiography and Imaging on the Central Coast: A Guide
Science radiography applies proven imaging methods to help clinicians diagnose, monitor and guide treatment. Using controlled X-rays, sound waves and specialised detectors, we create internal views of the body to answer clinical questions. This guide explains the core science behind common modalities — digital X‑ray, CT, ultrasound and DEXA — and how each fits into care pathways. You’ll find clear pre-scan checklists, concise answers to common questions, and practical comparison tables to help patients and referrers prepare and book local appointments. Throughout we stress safety (including ultra‑low‑dose CT), choosing the right modality for common conditions, and simple booking steps to turn intent into appointments at Life Medical Imaging Central Coast.
What Is Science Radiography and How Does It Support Medical Imaging?
Science radiography is the medical discipline that uses controlled energy (X‑rays or sound) and detectors to produce diagnostic images. These images reveal anatomy, detect pathology and show function — helping clinicians make informed decisions. The process relies on energy passing through tissue, differences in attenuation or echo response, and digital reconstruction to turn signals into readable images. The main benefit is targeted, non‑invasive visualisation that guides diagnosis, treatment planning and minimally invasive procedures while limiting patient burden. Knowing the strengths of each modality helps referrers and patients pick the right study. Below is a compact reference describing common modalities, how they work and typical clinical uses for quick selection.
Each modality offers particular diagnostic strengths via distinct physical mechanisms and clinical applications.
This table links modality mechanisms to practical uses and leads into a closer look at how images are obtained and the roles radiographers and radiologists play in quality and safety.
Science radiography depends on accredited equipment and trained staff to deliver reliable results. Understanding the role of radiographers, sonographers and radiologists clarifies how images are acquired, reported and acted on — and frames the booking, preparation and safety steps clinicians and patients need to follow.
How Does Radiography Work in Diagnostic Imaging?
Radiography creates diagnostic images by applying energy that interacts with tissue and recording the resulting signal. For X‑ray methods this is differential attenuation; for ultrasound it’s reflected sound processed into moving images. Digital detectors convert X‑ray photons into electronic signals that reconstruction software turns into detailed images. Ultrasound transducers send pulses and measure echoes to show anatomy and motion in real time. Radiographers and sonographers set acquisition parameters, position patients and manage exposure to balance image quality and dose. Radiologists then interpret the images and produce structured reports for referring clinicians. Knowing these steps explains why preparation, positioning and prior imaging affect diagnostic yield and sets up the modality‑specific sections that follow for the Central Coast.
Radiation physics and acoustic imaging form the technical basis for choosing and optimising studies — a foundation for clinical decision‑making covered later.
What Are the Key Imaging Modalities in Science Radiography?
The main modalities are digital X‑ray, CT, ultrasound, DEXA and interventional imaging. Each uses different hardware and gives complementary information. Digital X‑ray is fast and excellent for bone and chest views; CT delivers cross‑sectional anatomy and detailed soft‑tissue contrast; ultrasound is radiation‑free and ideal for dynamic assessment of organs, vessels and MSK structures; DEXA measures bone density and body composition with very low dose. Interventional techniques combine imaging and treatment to perform precise, minimally invasive procedures. Choosing the right test balances diagnostic accuracy, patient safety and the clinical question — matters addressed in the preparation and booking guidance below.
Placing these modalities into clinical pathways shows how radiography supports diagnosis, staging, intervention and long‑term monitoring across specialties.
How Can You Book a CT Scan Appointment in Erina and What Should You Expect?

To book a CT in Erina you’ll need a referral from a clinician. Appointments can be made via our online booking system or arranged by your referrer. The booking process confirms the clinical indication, selects the correct CT protocol and completes safety checks. CT works by rotating an X‑ray source and detector around the body while reconstruction software creates cross‑sectional images. Modern ultra‑low‑dose protocols and advanced reconstructions reduce radiation while keeping diagnostic detail. CT’s strengths are rapid coverage of large areas, excellent spatial and contrast resolution for complex problems, and specialised studies such as CT angiography or Cardiac CT when required. On the day expect quick registration, positioning on the CT couch, and a scan time from a few minutes up to 30 minutes depending on contrast and protocol. If contrast is used, a radiologist will review the images and a report is sent to your referrer.
- Have a valid referral that clearly states the clinical question.
- Request an appointment through Life Medical Imaging Central Coast’s online booking or ask your referrer to schedule it.
- Follow any pre‑scan instructions for contrast (fasting, kidney checks), bring referral and ID, and allow 10–30 minutes for the scan.
These steps outline what patients and referrers should do. The following paragraphs explain low‑dose CT benefits and offer specific preparation details for our Erina service.
A short comparison of CT types helps choose the right protocol for each clinical need.
Book your CT appointment: Arrange CT scans in Erina via Life Medical Imaging Central Coast’s online booking or ask your referring clinician to submit a booking request. Follow any pre‑scan instructions provided by the clinic and bring your referral and any prior imaging on the day. The next section outlines why low‑dose CT matters for safety and diagnostic quality.
What Are the Benefits of Low-Dose CT Scans in Radiology?
Low‑dose CT reduces ionising radiation by combining optimised acquisition settings, sensitive detectors and advanced reconstruction methods that preserve image detail. Modern iterative and AI‑assisted reconstructions improve signal‑to‑noise, allowing fewer photons without losing clinically useful contrast. Low‑dose protocols are especially important for surveillance studies, lung screening and paediatric imaging where cumulative exposure is a concern, while still providing accurate diagnostic information for many indications. Understanding these trade‑offs helps referrers select the appropriate protocol; the next subsection covers concrete preparation steps for CT at Life Medical Imaging Central Coast.
How Should Patients Prepare for a CT Scan at Life Medical Imaging Central Coast?
Preparation depends on the CT type and whether contrast is required. For non‑contrast exams, wear comfortable clothing and bring your referral. For contrast studies you may need a short fast, recent kidney function tests and to advise us of any allergies. If you have a previous reaction to contrast, tell your referrer and our team so we can consider pre‑medication or an alternative test. Pregnant patients should discuss risks with their clinician before booking. Always bring any prior imaging for comparison and follow any medication instructions given at booking. Good preparation reduces the need for repeat scans and improves diagnostic accuracy.
To book CT in Erina: use our online booking or ask your referring clinician to request an appointment, and follow any pre‑scan instructions sent by the clinic.
What Ultrasound Services Are Available at Central Coast Clinics and How Do They Work?
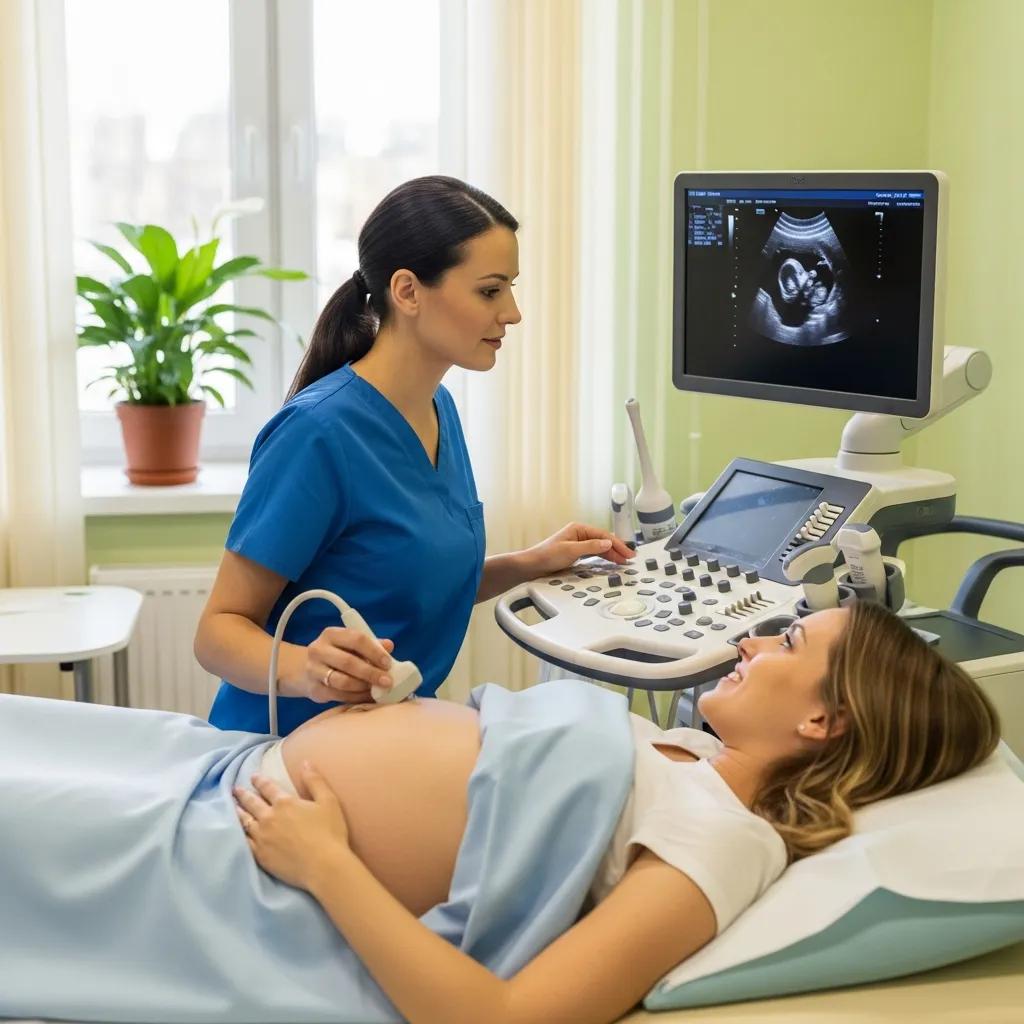
Ultrasound uses high‑frequency sound waves from a transducer that reflect off tissues to create real‑time images. This radiation‑free modality is ideal for assessing organs, blood flow and soft tissues dynamically. Image formation depends on differences in acoustic impedance between tissues; Doppler techniques assess flow. Ultrasound is portable, safe for repeated use (including pregnancy), and commonly used for image‑guided procedures without ionising radiation. Below are the main ultrasound types with a brief mechanism and primary clinical use for quick reference.
Common ultrasound types and their core indications to help referrers and patients choose the right exam.
- Obstetric ultrasound: sound‑wave imaging to assess fetal growth and anatomy.
- Vascular ultrasound: Doppler evaluation of blood flow to detect DVT or carotid disease.
- Musculoskeletal (MSK) ultrasound: dynamic imaging of tendons, ligaments and soft tissues.
- Gynaecological ultrasound: pelvic organ assessment and follicle tracking.
These labels guide modality selection and lead into preparation instructions for typical ultrasound exams.
Ultrasound preparation varies by exam — the list below summarises common steps to ensure clear imaging.
- Abdominal Ultrasound: Fast for 6–8 hours to reduce bowel gas and improve organ visualisation.
- Pelvic/Obstetric Ultrasound: Arrive with a comfortably full bladder for early pregnancy and pelvic views.
- Vascular/MSK Ultrasound: Wear loose clothing and bring relevant clinical notes; fasting is usually not needed.
These preparation tips help patients arrive ready and shorten scan times. The next section explains how to book and what to expect at our Central Coast clinics.
Book your ultrasound appointment: Use Life Medical Imaging Central Coast’s online booking or ask your referring clinician to arrange the study. Follow any exam‑specific instructions for fasting or bladder fill and bring your referral and relevant clinical history.
What Types of Ultrasound Scans Does Science Radiography Include?
Ultrasound services cover obstetric, gynaecological, vascular and musculoskeletal imaging, each tuned by transducer selection and technique to the clinical question. Obstetric scans monitor fetal development and wellbeing. Gynaecological ultrasound evaluates uterine and ovarian conditions and supports fertility work‑ups like follicle tracking. Vascular studies use Doppler to assess blood flow and detect occlusion or stenosis. MSK ultrasound visualises tendons, ligaments and small joint pathology and can be performed dynamically. Paediatric ultrasound adapts frequency and technique for smaller anatomy. These distinctions guide appropriate test selection and practical preparation advice below.
How Do You Prepare for an Ultrasound Appointment at Central Coast Clinics?
Preparation depends on the area being scanned: abdominal studies usually require fasting to reduce bowel gas; pelvic and early pregnancy scans typically need a full bladder for better views; vascular and MSK scans usually require only comfortable clothing. Specific instructions are provided with your appointment. Patients having serial studies for fertility (follicle tracking) will receive timing details from their clinician. If you need mobility assistance or have recent surgical notes, tell the clinic in advance so staff can prepare. Clear preparation improves image quality and shortens appointment times.
Why Choose Digital X-Ray Services in NSW for Accurate Diagnostic Imaging?
Digital X‑ray delivers high‑resolution planar images with fast acquisition, immediate review and efficient electronic storage. Digital detectors capture X‑ray photons and convert them to electronic signals that can be enhanced, dose‑tracked and shared securely for reporting. This makes digital X‑ray ideal for musculoskeletal trauma, chest imaging and dental panoramic (OPG) studies where sharp bone detail and quick turnaround matter. Compared with film, digital systems reduce repeat rates, allow exposure optimisation to lower dose and speed report delivery to referring clinicians. The paragraphs below offer a direct comparison and case examples to help choose the best test.
Digital X‑ray’s advantages over film improve workflow, image quality and patient safety for common clinical indications.
Book your digital X‑ray appointment: For suspected fractures, chest X‑rays or dental OPGs request an appointment via Life Medical Imaging Central Coast’s online booking or have your referrer arrange it. Bring your referral and any prior images for side‑by‑side comparison and faster diagnosis.
What Are the Advantages of Digital X-Ray Over Traditional X-Ray?
Digital X‑ray lowers radiation exposure by enabling precise exposure settings and fewer repeat images because acquisition feedback is immediate. The detector‑to‑software workflow allows contrast adjustment and magnification to highlight subtle findings. Electronic PACS storage enables secure sharing and longitudinal comparisons. These benefits speed diagnosis, reduce dose and improve coordination with referring teams — important reasons to choose digital imaging when available.
How Is Digital X-Ray Used for Bone Fractures and Dental Imaging?
For fractures, targeted digital X‑ray views and standardised positioning reveal fracture lines, joint involvement and alignment; multiple projections increase sensitivity and guide treatment such as casting or surgical referral. Panoramic OPGs offer a full jaw overview for dental surgery planning, third‑molar assessment and orthodontic review, while intraoral sensors provide high‑resolution per‑tooth detail. Radiographers follow exposure charts and positioning protocols to ensure diagnostic, reproducible images; radiologist review confirms fracture character, alignment and any occult injuries. Clear imaging protocols improve triage and treatment planning and connect patients to local specialist care.
What Specialized Radiology Services Does Life Medical Imaging Offer in Gosford and Central Coast?
Life Medical Imaging Central Coast offers a wide range of specialised outpatient services across multiple locations: Bateau Bay, Killarney Vale, Umina Beach, Erina and Gosford. Our services support complete diagnostic pathways and include General CT, Cardiac CT and CT Angiography, comprehensive ultrasound (obstetric, vascular, MSK, gynaecological), Digital X‑ray including OPG, dedicated Paediatric Imaging, DEXA bone density and body composition, plus interventional procedures such as spinal and joint injections, biopsies and aspirations. We prioritise ultra‑low‑dose protocols, high‑definition equipment and experienced clinical staff to deliver accurate results with patient safety and comfort in mind. This service overview helps referrers select the most appropriate local site for each patient.
Key specialised services and their clinical value, summarised for referrers and patients.
- Cardiac CT & CT Angiography: non‑invasive assessment of coronary and vascular anatomy.
- Paediatric Imaging: child‑friendly protocols and radiation‑sparing techniques.
- Interventional Procedures: image‑guided injections and biopsies for diagnosis and treatment.
Book your specialised imaging appointment: To arrange Cardiac CT, paediatric studies, DEXA or image‑guided procedures ask your referrer to request an appointment with Life Medical Imaging Central Coast or use our online booking system. With multiple Central Coast locations you can choose the most convenient site for the required service.
How Does Women’s Imaging Enhance Diagnostic Accuracy in Science Radiography?
Women’s imaging — including breast ultrasound, gynaecological ultrasound and follicle tracking — uses tailored protocols and specialist sonographers to improve lesion characterisation and guide follow‑up. Breast ultrasound complements mammography by distinguishing cysts from solid lesions and helping guide biopsies. Pelvic scans evaluate structural pathology, early pregnancy and fertility monitoring with dynamic assessment. Specialist training and focused reporting reduce false positives, speed referral to breast or gynaecology clinics and improve patient outcomes.
What Are the Features of Paediatric and Cardiac Imaging Services?
Paediatric imaging uses child‑appropriate equipment, lower exposure settings and communication techniques to minimise radiation and anxiety while maintaining diagnostic quality. Cardiac imaging services include Cardiac CT and vascular studies that provide high‑resolution images of coronary anatomy, vessel patency and cardiac structure — often using ECG‑gating to reduce motion artefact. Both services follow specific preparation protocols (e.g. heart‑rate control for cardiac CT) and integrate with local cardiology and paediatric pathways to deliver timely results.
Paediatric Body Composition Analysis Using Dual‑Energy X‑ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
Dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry (DXA) can measure fat mass (FM) and lean tissue mass (LTM) alongside bone mineral content (BMC). Among accessible body composition techniques, DXA is widely used and provides precise regional FM and LTM quantification.
Pediatric body composition analysis with dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry, 2009
How Do Interventional Radiology Procedures and Bone Densitometry Support Patient Care on the Central Coast?
Interventional radiology offers minimally invasive treatments and diagnostic sampling guided by imaging, targeting pathology precisely while reducing recovery time compared with open surgery. Common procedures include spinal injections for pain relief, joint injections for symptom control, and image‑guided biopsies and aspirations for tissue diagnosis. These procedures use ultrasound, fluoroscopy and CT for accurate needle guidance and immediate monitoring. DEXA complements intervention by measuring bone mineral density and body composition to guide fracture risk management, medication decisions and baseline assessment before therapies.
Core interventional and DEXA services in plain terms:
- Spinal and joint injections: targeted pain relief and diagnostic response testing.
- Biopsies and aspirations: minimally invasive tissue sampling under image guidance.
- DEXA scanning: bone mineral density and body composition metrics to assess fracture risk.
Book interventional or DEXA services: To enquire about spine injections, image‑guided biopsies or DEXA scans ask your referrer to request an appointment at Life Medical Imaging Central Coast or use our online booking. Follow any pre‑procedure instructions and tell us about anticoagulant use or relevant medical history.
What Are Common Interventional Procedures Offered in Science Radiography?
Common interventional procedures include spinal steroid or diagnostic injections for radicular pain, ultrasound‑guided joint injections for arthritis flares, and percutaneous biopsies for tissue diagnosis in suspected tumours or inflammatory lesions. These image‑guided techniques deliver precise therapy with lower complication rates than open surgery and allow quick outpatient recovery. Patients usually receive local anaesthetic and brief monitoring post‑procedure; follow‑up is arranged with the referring clinician and radiology team. Knowing indications and expected recovery helps referrers and patients weigh interventional options against conservative or surgical care.
How Does a DEXA Scan Help Assess Bone Health and Body Composition?
DEXA measures bone mineral density (BMD) using low‑dose dual‑energy X‑rays to produce T‑scores and Z‑scores used in osteoporosis diagnosis and fracture risk assessment. It also provides body composition data such as lean mass and fat distribution. Standard interpretation thresholds are: T‑score ≤ −2.5 (osteoporosis), −1.0 to −2.5 (low bone mass/osteopenia), and ≥ −1.0 (normal). DEXA preparation is minimal — avoid calcium supplements on the day and wear clothing without metal — and results are used alongside clinical assessment to plan prevention or treatment. This objective measure complements interventional and medical strategies for patients at risk of fragility fractures.
DXA for Body Composition Analysis: Fat Mass, Lean Mass and Bone Mineral Content
Dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry (DXA) can be used to determine fat mass (FM) and lean tissue mass (LTM), as well as bone mineral content (BMC). Of the widely available body composition analysis techniques, DXA is commonly used and accurately quantifies regional FM and LTM.
Dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry and body composition, LD Plank, 2005
DEXA’s ability to quantify regional fat and lean mass makes it a useful tool for body composition analysis in many clinical settings.
DXA for Body Composition Assessment: Fat, Lean Mass and Bone
This review outlines the use of dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry (DXA) for overall and regional body composition assessment of fat, lean mass and bone. DXA is widely used in clinical practice, primarily for diagnosing osteoporosis.
Body composition assessment by dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry (DXA), 2009
Each service supports coordinated care pathways, and clear booking options help turn diagnostic intent into timely appointments across convenient Central Coast locations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a CT scan and an MRI?
CT and MRI are different imaging technologies. CT uses X‑rays to create cross‑sectional images and is excellent for visualising bone, acute trauma and many cancers. MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues — useful for the brain, spinal cord, joints and some internal organs. The choice depends on the clinical question, patient factors and what information the referring clinician needs.
Are there any risks associated with radiographic imaging?
Imaging involving ionising radiation (X‑rays and CT) carries a small exposure risk, but modern techniques use low‑dose protocols to keep exposure as low as reasonably achievable while maintaining diagnostic quality. Ultrasound and MRI do not use ionising radiation and are typically safer alternatives when appropriate. Discuss any concerns with your clinician so they can explain the benefits and risks for the recommended test.
How can I access my imaging results?
Imaging results are usually sent to your referring clinician, who will review the report with you. Many centres, including Life Medical Imaging Central Coast, also provide online portals where patients can view reports and images. Ask about result access when you attend or contact the clinic for instructions on how to retrieve your report. Always follow up with your clinician to discuss next steps.
What should I do if I have a known allergy to contrast media?
If you have a known contrast allergy, tell your referring clinician and the imaging team before your appointment. We may recommend pre‑medication to reduce reaction risk or consider alternative imaging that does not require contrast. Provide a full history of previous reactions so the team can plan safely for your scan.
Can children undergo radiographic imaging safely?
Yes. Children can safely undergo imaging when appropriate. Facilities like Life Medical Imaging Central Coast use paediatric‑specific protocols to minimise radiation and employ child‑friendly techniques to reduce anxiety. Staff are trained to adapt communication and equipment for children. Discuss any concerns with your referrer or the imaging team so we can make the experience as safe and comfortable as possible.
What is the role of a radiologist in the imaging process?
A radiologist is a medical doctor specialised in interpreting imaging studies and providing diagnostic reports. After images are acquired, the radiologist reviews them, issues a structured report and advises the referring clinician. Radiologists also perform image‑guided interventional procedures and collaborate with other specialists to guide patient care.
How do I prepare for an ultrasound appointment?
Preparation depends on the scan type. For abdominal ultrasound you’ll usually be asked to fast for 6–8 hours to reduce bowel gas. For pelvic or obstetric scans, a comfortably full bladder is often required for early pregnancy views. Follow the specific instructions given at booking to ensure the best diagnostic quality.
Conclusion
Knowing how science radiography works helps patients and clinicians choose the right imaging at the right time. Modalities such as CT, ultrasound and digital X‑ray each serve specific clinical needs; prioritising safety and correct preparation improves the imaging experience and outcomes. To view our full range of services or to book an appointment, visit Life Medical Imaging Central Coast.